Deep Ocean Benthic Organisms Most Often Feed on
Benthic organisms are often deposit feeders obtaining nutrition from ingesting biota organic and inorganic particles from the sediment surface or within the sediments. DEEP OCEAN BENTHIC ORGANISMS FEED ON NERITIC ZONE MOST PRODUCTIVE BARRIER REEFS FORMED FROM THE REDUCTION OF OXYGEN AND NUTRIENTS CARRIED BY THE OCEAN TO FRINGE REEFS MIGRATING BIRDS USE SALT MARSHES FOR FEEDING WINTER HABITAT AND RESTING LIVING ORGANISMS TOP LAYER OF CORAL REEF ESTUARIES RINGED BY SALT.
What are the 2 main methods of feeding in this aria.

. Recent research indicates that the diversity of species living in the deep-sea may rival the species richness found in tropical coral reefs. Among the most common large deep-sea benthic deposit feeders are Sea cucumbers. The water contains about 3 percent salt mostly sodium chloride a factor that strongly affects the biology of the organisms that live there.
Whales which have to breath air may dive deep to feed near the ocean bottom but they dont live there. Deep-ocean benthic organisms most often feed on. Many sea cucumbers are deposit feeders - taking in the soft sediments digesting the organic material and infauna in the sediment and leaving behind cleaned sediment.
The lanternfish is by far the most common deep-sea fish. The low tide zone is home to the greatest number of soft-bodied organisms and marine algae. Other deep sea fishes include the flashlight fish cookiecutter shark bristlemouths anglerfish viperfish and some species of eelpout.
Most of the ocean is cold and dark. Tiny pieces of dead organic material that are food for organisms at the base of an aquatic food web are called detritus. Benthic Animals of the Deep Ocean BasinSediment Covered Shore WSHow a Baloney Sandwich Changed the way we think About the Deep Ocean1.
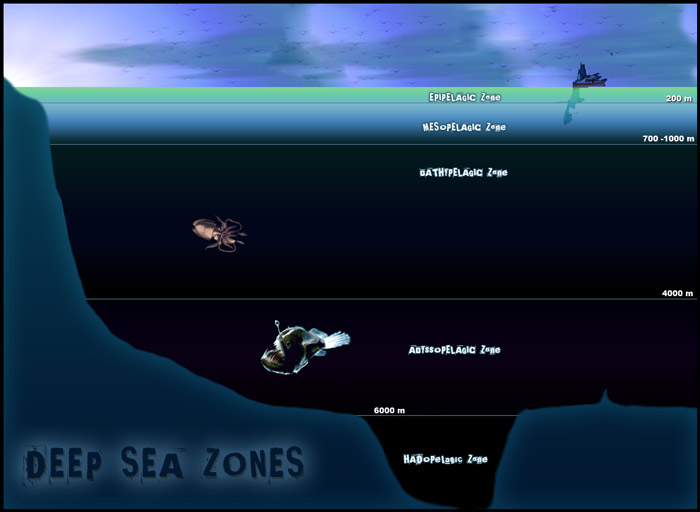
The oceanic zone is very deep ranging from about 200 m along continental slopes to as deep as 11000 m below the surface. Only about 2 of known marine species inhabit the pelagic environment. Which level of consumer had access to the smallest apply of energy.
- solid rock bouldery gravelly sandy silty muddy and clay. Typical benthic invertebrates include sea anemones sponges corals sea stars sea urchins worms bivalves crabs and many more. Marine snow provides a large proportion of the food for many of the deep-sea benthic species.
The distribution of benthic biomass closely matches the distribution of ________ in surface waters. RQQ An important predator of mussel beds in the middle tide zone is the _________. A scavenging amphipod with an expandable gut Unusual shrimp found around some Atlantic hydrothermal vents have light-sensitive patches on their upper surface that may help them find vents.
The deepest parts of the ocean are about 11 km 68 mi deep. Sunlight does not penetrate very deeply into the oceanic zone. 2 Show answers Another question on Biology.
Be notified when an answer is posted. The spray zone is where organisms with shells are mostly found. What do Deep-ocean benthic organisms most often feed on.
Another important factor affecting marine organisms is the availability of light. Sea cucumbers are a common epifaunal animal found on soft bottoms. What part of the deep ocean basin did Alvin most likely land on2.
Many species particularly polychaete worms ingest subsurface sediments and convey them to the sedimentwater interface as fecal pellets. High level continental shelves below high productivity areas. Want this question answered.
Which statement best describes how the loudness of the sound affects the high-pressure region created. Benthic creatures live on the bottom of the ocean. Which of these animals probably lives on the deep-sea floor.
Most benthic organisms occur in the photic zone or below the photic zone. Most organisms in the ocean are benthic.

Life In The Deep Sea Let S Talk Science
Comments
Post a Comment